Standard: IEC 60831-1 Shunt Power Capacitors of the Self-Healing Type for A.C. Systems Having a Rated Voltage up to and Including 1000V.
POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
Power factor is the ratio of real power in Kilowatts (kW) flowing into a load to the apparent power in Kilovolt-amperes (kVA). An electrical system with high power factor will lose less energy compared to a system with low power factor
Electrical equipment that have windings like motors, welders, etc., can cause delay to current flow as compared to voltage. Such electrical equipment cause a lagging power factor. That’s why for industrial plants, power factor is an indicator of the efficiency with which the load utilizes the available power.
The industry standard power factor is 85%. Energy Regulatory Board regulates the rate schedule of utility company which penalizes power factor lower than 85% while give a discount or reward for power factor higher than 85%.
While there are equipment causing a lagging power factor, the use of capacitor can advance the current to voltage to cancel the reactive current of the equipment.
Advantages of Installing Capacitors
- Power cost saving
- Reduce the power loss
- System capacity enforcement
- Stable voltage
Selection of Capacitor
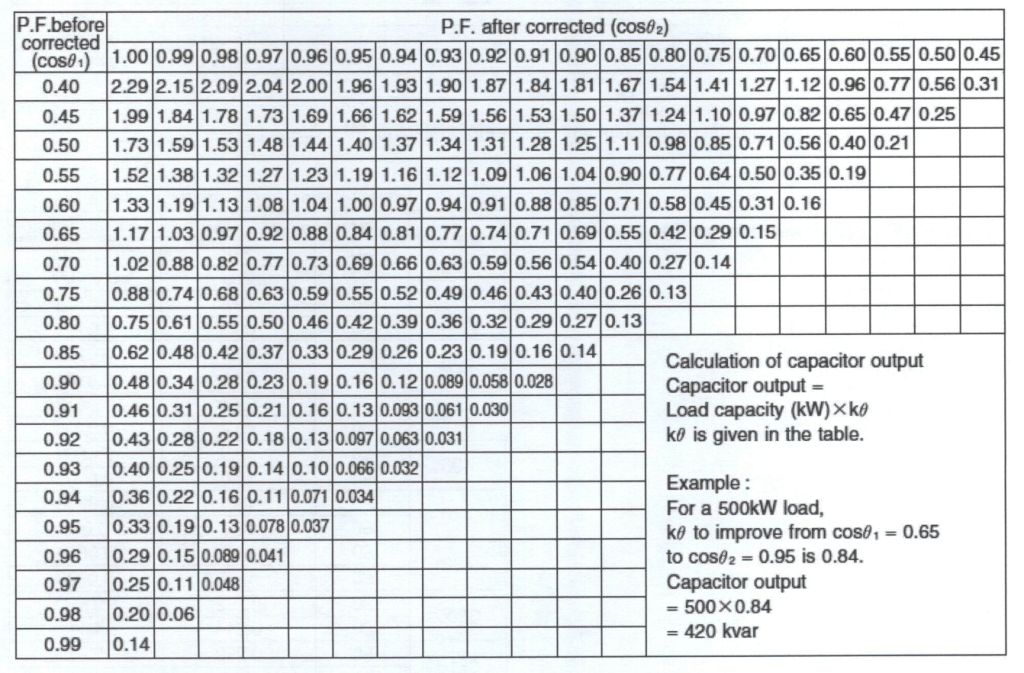
The KVAR rating of power capacitors can be obtained by the following formula:
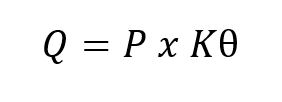
Where:
Q = KVAR rating of a capacitor to be installed
P = KW Capacity of load
K = Output factor to be calculated by the following formula:
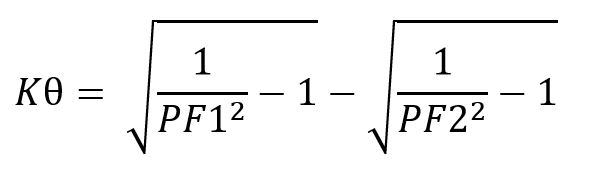
Where:
PF1 = Power factor BEFORE improving
PF2 = Power factor AFTER improving
Sample
For example, for a 500kW load, we want to improve the power factor from 0.65 to 0.95.
Substituting PF1 = 0.65 and PF2 = 0.95 to the formula, we will get K = 0.84.
Capacitor Rating, Q = P x K = 500kW x 0.84
Capacitor Rating = 420kvar